
All you need to know about
Herniated discs
Why should you, as a patient or prospective patient, be informed? It’s all about you and your back.
Available soon…
You are the principal actor of your surgery
You will be the only one present from the beginning to the end of the care process, from A to Z and beyond that, you’ll have to live with it. In other words, you need to be part of the project, part of the surgical team. To feel at ease within this team, it’s essential to inform you and give you the keys to communicating as well as possible with the caregivers.
What is sciatica or cruralgia?
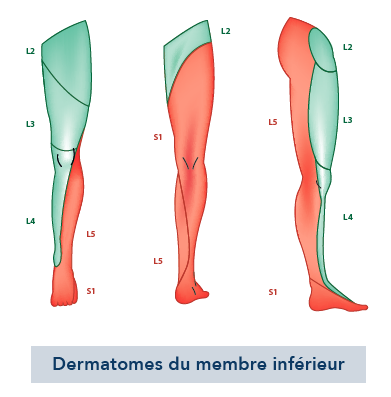
Sciatica or crural pain is pain secondary to nerve root compression. Cruralgia corresponds to compression of the L2, L3 and L4 nerve roots. Sciatica corresponds to compression of the L5 and S1 nerve roots. Depending on which nerve root is compressed, the site of pain is different (see diagram). The area of sensitivity (“territory”) dependent on a nerve root is called the dermatome.
Why operate on a hernia?
Apart from surgical emergencies (as described below), the primary treatment for herniated discs is medical, not surgical. Most herniated discs (over 80%) resolve within a few weeks. The diagnosis of a herniated disc, suspected by questioning and clinical examination, is confirmed by MRI of the lumbar spine. The surgeon checks that there is a match between your pain and the lesions visible on the MRI.
Discectomy surgery (removal of the herniated disc) is proposed when conservative treatments such as medication, lumbar belt, infiltrations and/or re-education are no longer effective. Sciatica (pain in the territory of the sciatic nerve) or cruralgia (pain in the territory of the crural nerve) have then become too incapacitating. Surgery can relieve the pain. However, there are a few special cases where the severity of the symptoms calls for rapid intervention:
– Proven motor deficit. Muscles in the foot, leg or thigh no longer function properly.
– Ponytail syndrome. The sphincters no longer function properly and/or the perineum is anaesthetized.
– Hyperalgesia. The pain of sciatica or cruralgia is intolerable and not relieved by morphine.
These symptoms indicate severe damage to the nerve roots. Symptoms can be improved by immediate surgical intervention. During your consultation, your surgeon will ask you questions and test your reflexes and muscle strength in your lower limbs, looking for these complications.
How do you prepare for the procedure?
You may be surprised at the time between the first consultation and the date of the operation, but meticulous preparation reduces the risk of most early or late complications. An operation, just like a competition, an important event or a long journey, needs to be prepared!
This includes a medical check-up, an appropriate diet and psychological, material and physical preparation, such as learning new movement patterns, breathing exercises, wearing a neck brace or pelvic belt ….
